
NUF - Niigata University Forest -
Field Center for Sustainable Agriculture and Forestry,
Faculty of Agriculture, Niigata University

Location & Topography
The Niigata University Forest (NUF) is located on northern part of Sado Island (855 km2). Sado Island is 50km far from Niigata City and it takes 150 minutes by the ferryboat. The island has never been connected to the main land Honshu since it was born, and some endemic and / or endangered species are distributed. The island has very high climate diversity because of two different marine streams (warm stream from south and cold stream from north), strong winter wind from the continent and heavy snowfall. Northern part of the island is relatively high mountains (Ohsado Mountains; ca. 1000m a.s.l.) and covered with cool temperate vegetation, while Southern part has lower mountains (Kosado Mountains; ca. 450m a.s.l) and warm temperate vegetations.
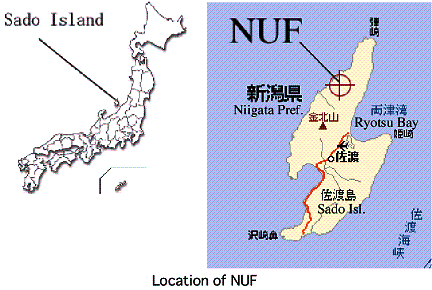
NUF and Kosado branch
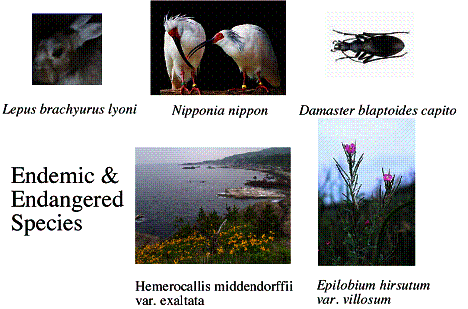
Faculty of Agriculture of Niigata University has two stations on the island. One is NUF (500ha) located on Osado Mountains. NUF was found on 1955 and it has been used mainly for education and research of forestry and forest science. NUF has been noted for huge, long-lived conifer timbers (Cryptmeria japonica), two endemic mammals (Lepus brachyurus lyoni and Sorex sadonis), an endemic beetle (Damaster blaptoides capito), and many endangered perennial flowers. Two investigators and five technicians are engaged in the station. Kosado Branch (30ha) founded on 2002 is located on southern part of the island. This branch was found to take in part with a national project to reintroduce an endangered bird, Japanese Crested Ibis (Nipponia nippon). These endemic and endangered species are the supreme character of NUF.
Site policy and activities
The aim of NUF is to understand the ecology of special creatures mentioned above and ecosystems of this island, and to utilize them for environmental education.
As a member of JERN-JaLTER, NUF has been conducted long-term study of community dynamics of Cryptmeria japonica forest, climate monitoring and hydrologic studies. Study themes are mainly on the relationships between disturbances (or environmental stresses) and forest regeneration because the ecosystem of NUF is heavily affected by the strong wind and heavy snow in winter.
On the other hand, Kosado branch is promoting conservation and restoration ecology of agricultural ecosystems and coppices. In Japan, the biggest reason of serious biodiversity loss is succession of abandoned crop fields and coppices (Satoyama ecosystems). Many field experiments and monitoring related to the Japanese Ibis have been conducted in Kosado region and the results have been used for regional planning and education.
Abandoned old rice fields are going to be restored for keeping
biodiversity in the 'Satoyama' ecosystem of Kosado mountains.
※ 写真準備中
Osado Mountains (Mt. Kinpoku) in winter
※ 写真準備中
Contact us
Field Center for Sustainable Agriculture and Forestry, Faculty of Agriculture, Niigata University
Koda 94-2 Sado, Niigata 952-2206, Japan. E-mail:homma-k@f2.dion.ne.jp