Objectives and Outlines
Objectives

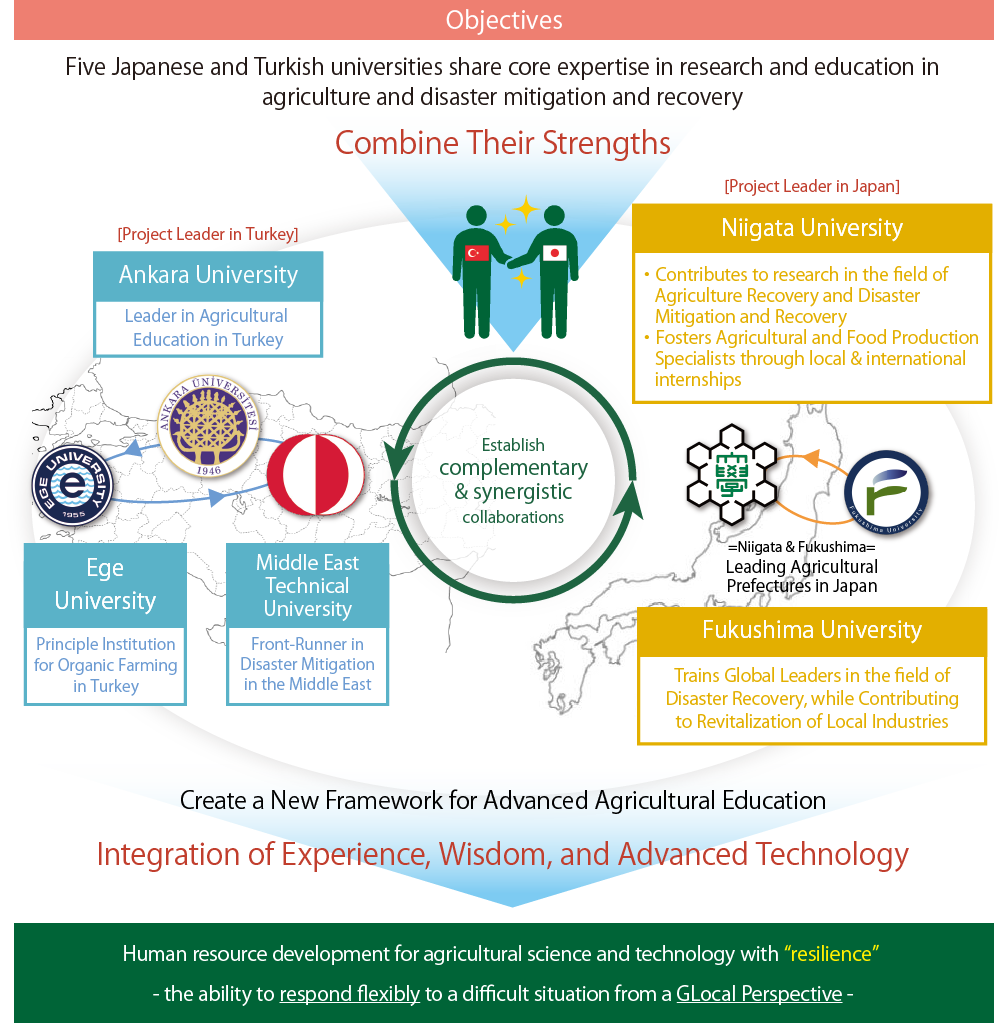
Project Leader in Turkey
 Ankara University
Ankara University- Leader in Agricultural Education in Turkey
 Ege University
Ege University- Principle Institution for Organic Farming in Turkey
 Middle East Technical University
Middle East Technical University- Front-Runner in Disaster Mitigation in the Middle East

Project Leader in Japan
 Niigata University
Niigata University- ・Contributes to research in the field of Agriculture Recovery and Disaster Mitigation and Recovery
・Fosters Agricultural and Food Production Specialists through local & international internships
 Fukushima University
Fukushima University- Trains Global Leaders in the field of Disaster Recovery, while Contributing to Revitalization of Local Industries

Human resource development for agricultural science and technology with “resilience”- the ability to respond flexibly to a difficult situation from a GLocal Perspective -
Objectives
The ability to respond flexibly, so-called “RESILIENCE,”to disasters and changes observed throughout the world has become a significant topic these days. Agriculture and food production in Japan and Turkey are commonly exposed to various disastrous risks, such as earthquakes, tsunami, and floods. Furthermore, both countries collaboratively need to work on easing the international regulations of the agricultural product markets.
Fostering resilient individuals who are able to respond to these problems comprehensively is essential in both countries. Therefore, this project aims to foster global agricultural specialists with resilience to respond to various difficult situations, by learning food science and disaster prevention technology with experience and wisdom of both countries and to develop the appropriate educational framework to achieve the goal.
Background
Turkey is considered one of the major agricultural countries in the world but is also a country with frequent disasters. Recently in Turkey, the intensive use of agricultural fields and soil deterioration due to desertification have become problems. A thought to utilize lands for disaster prevention is still under-developed, and the provision for natural disaster occurrence in agricultural field is very low. On the other hand, they value seeding in local regions and extending exportation of high quality organic crops and processed food to EU countries by implementing large-scale organic farming through recycling organic resources, such as straw.
Japan has been reconsidering effective disaster mitigation technology by use of traditional indigenous engineering since the Great East Japan Earthquake. We have been trying to strengthen farm village and agricultural infrastructure, such as gathering or expanding farms, depending on disaster mitigation needs in local level. Furthermore, Japan has been focusing on developing inexpensive but effective disaster mitigation technology by integrating basic technology, such as creating a hazard map on landslide and floods and a risk map on damages expected in preservation areas, and traditional local indigenous engineering. Additionally, we have been trying to strengthen the globalization through transformation to sustainable environmental conservation-type agriculture, including organic farming, and promoting the 6th industrialization which produces added value in organic food production.
Niigata and Fukushima are leading agricultural prefectures as well as natural disaster areas in Japan. Niigata University carries out a mission to foster agricultural specialists through practical education in fields and internship-oriented education and promotes local restoration through disaster mitigation and recovery learned from domestics and foreign countries.
Fukushima University trains global leaders with knowledge of agricultural economy, local restoration, and agricultural recovery.
Ankara University and Ege University are leading universities in education and research in sustainable agriculture and food production in organic farming, and students can learn the large-scale organic farming. Middle East Technical University is one of the best universities with disaster mitigation education in the Middle East, and the university is the most suitable education and research institution for indigenous engineering in Turkey.
This project aims to combine strengths of each of five universities to foster global specialists with resilience by integrating perspectives of agriculture, food science, disaster risk reduction and recovery and to develop the education framework for advanced agricultural education.
Outlines
In this project, the programs are available for both outbound and inbound undergraduate and graduate students with possible credit transfer. The available programs are: Short-Term Exchange Program (2-4 weeks); Intermediate-Term Exchange Program (3-5 months); and Long-Term Exchange Program (6-12 months).
Participating students from Turkey will learn advanced agricultural infrastructure, food science biotechnology, systems for disaster risk reduction and recovery including transmission and conservation of farms and residential lands and technology. On the other hand, participating students from Japan will learn large-scale management of organic farming, market development in EU, and indigenous engineering for disaster mitigation in Turkey.
Short-Term Exchange Program is designed as a GLocal Project-Based-Learning program in which students discuss local issues by applying a global perspective to potential solutions. Intermediate-Term and Long-Term Exchange Programs focus on research.
Inbound students from Turkey can participate in an internship at Foricafoods Corporation, specializing in emergency provisions and survival food, and other corporations. Outbound students from Japan can participate in an internship at Rapunzel, the large-scale organic farming corporation.
Human Resource Development
- We foster individuals with ability to solve problems by integrating experience, wisdom, and advanced technology of other countries
- We foster global leaders who contribute to the development of food science, disaster risk reduction and recovery, and economic development not only in Turkey and Japan but also world-wide